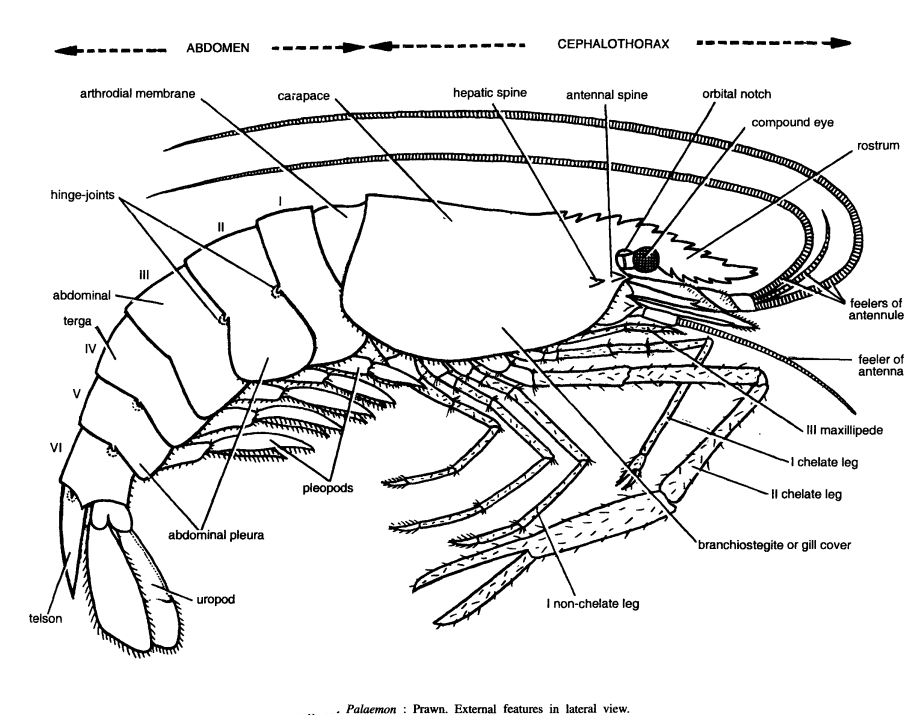
DISSECTION OF PALAEMON (PRAWN)
DISSECTION OF PALAEMON (PRAWN) External features of Palaemon (Prawn) It is fresh-water prawn, which forms a highly palatable dish. Prawn is the most favourite and well-liked animal by the students. Total length : 25 to 35 cm. Shape: Spindle-shaped, elongated and bilaterally symmetrical. Colour: Pale blue or greenish it becomes…