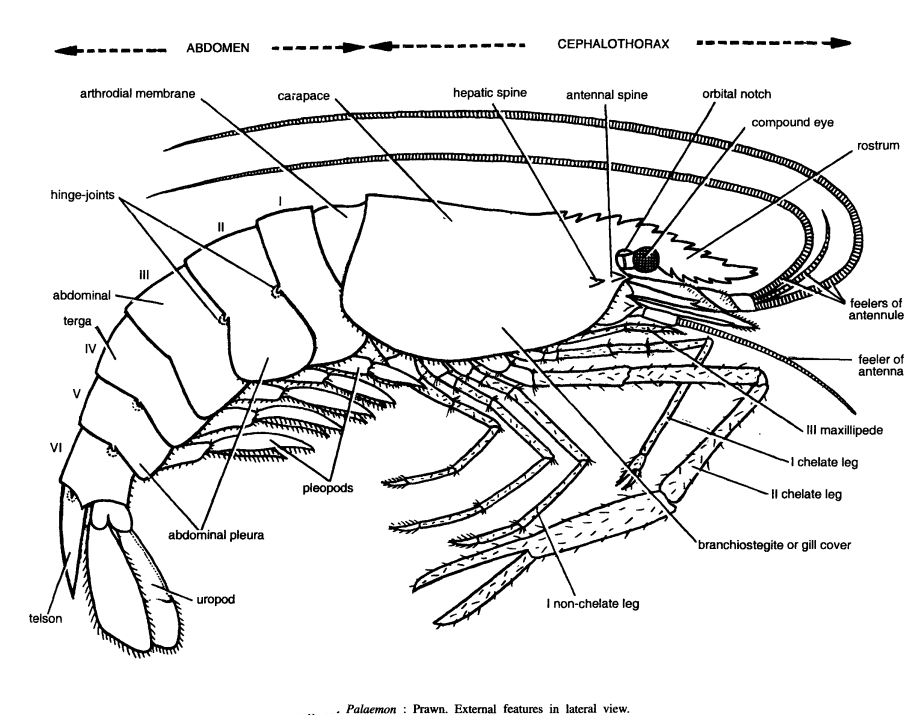
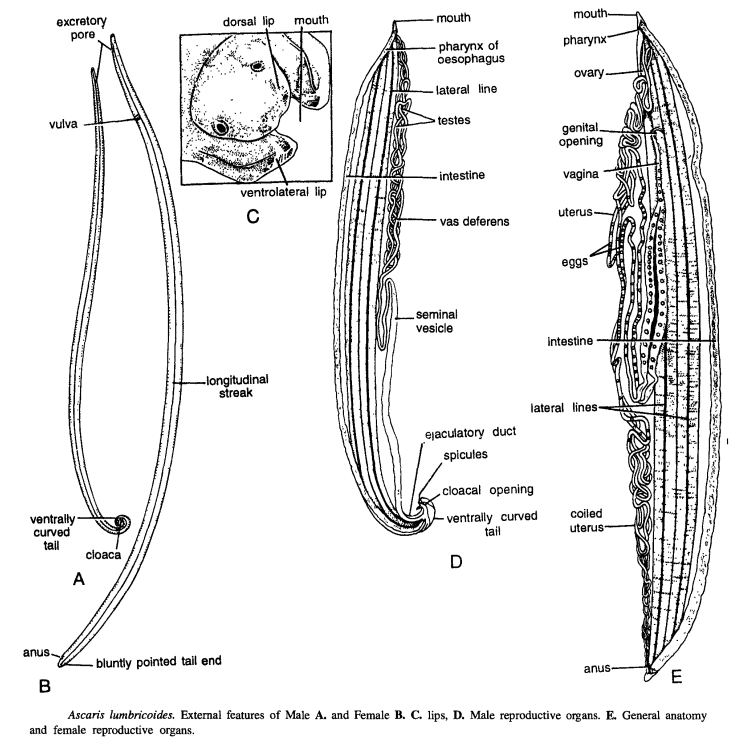
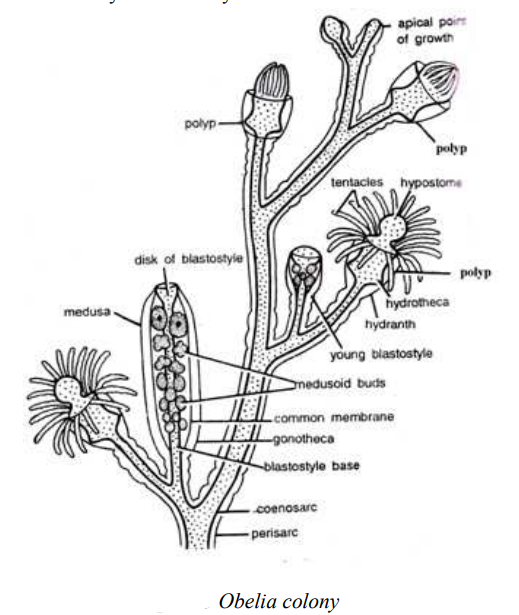
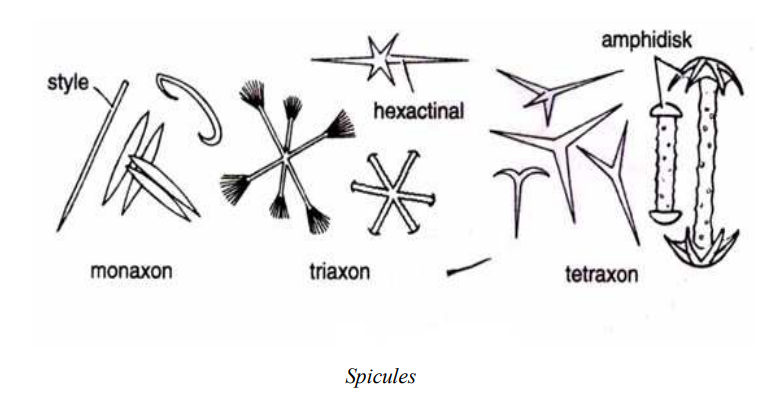
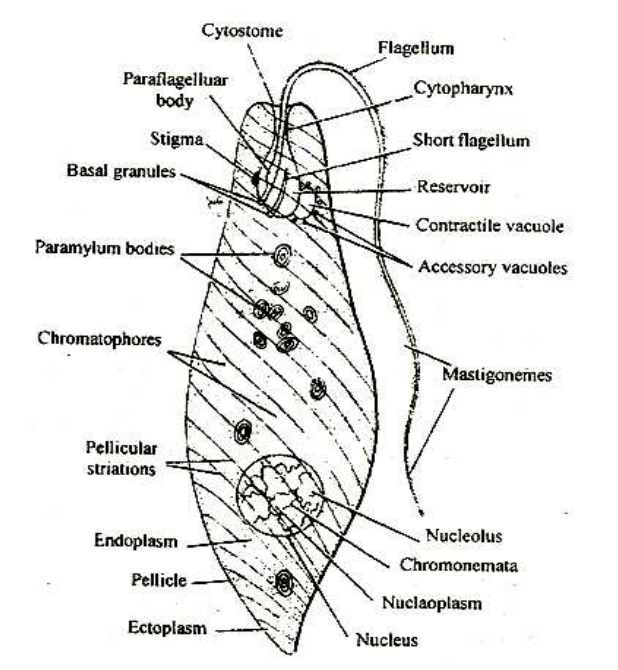
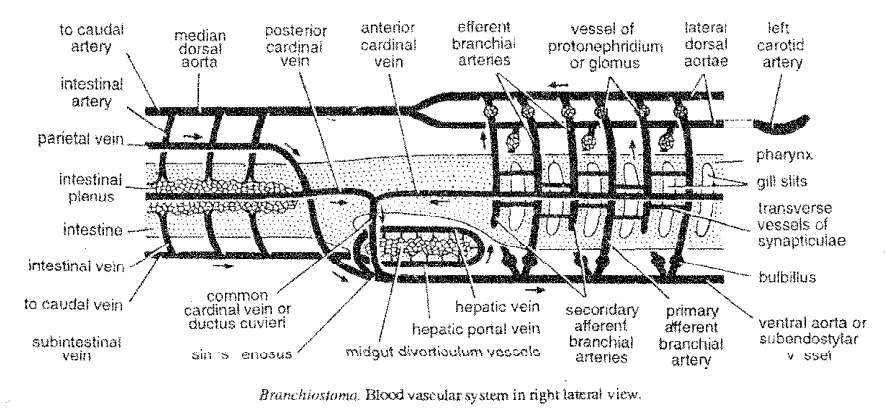
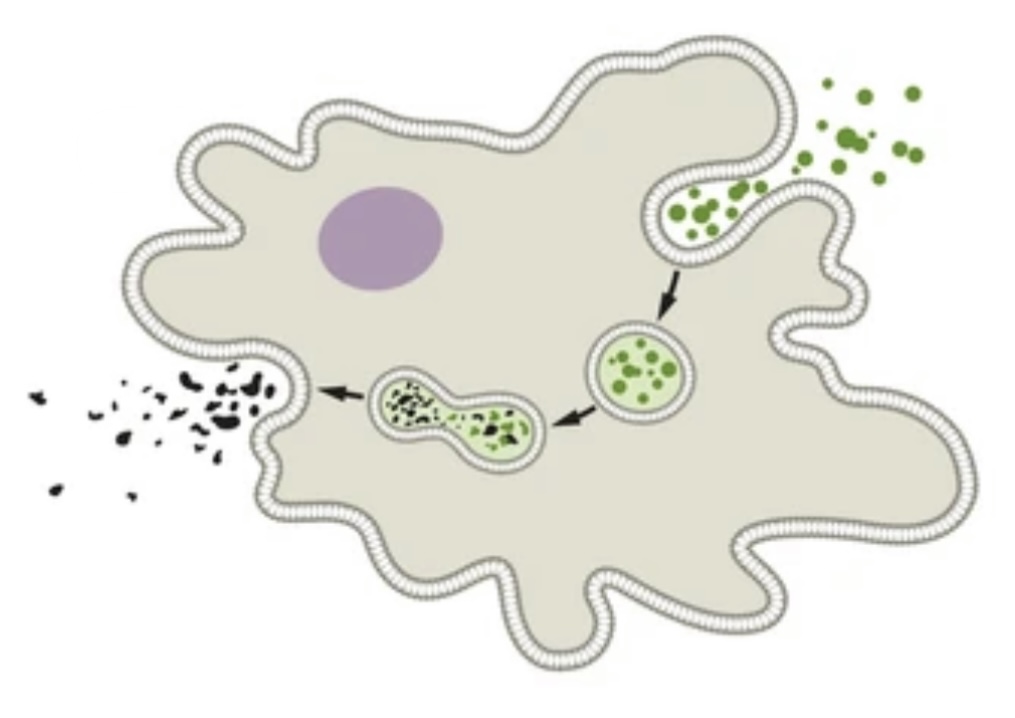
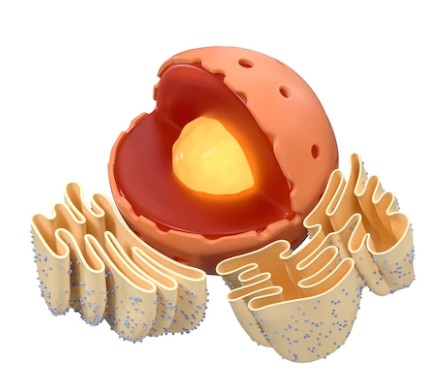
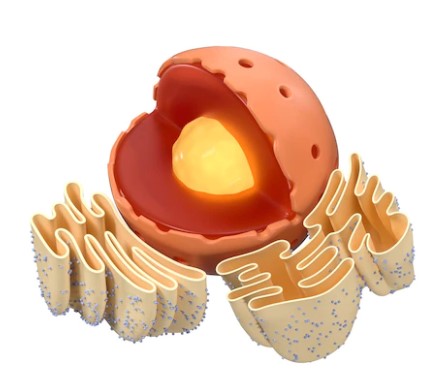
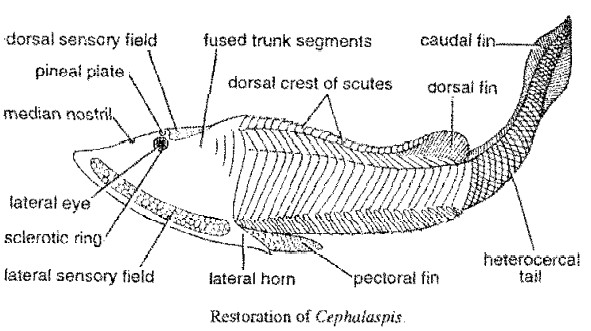
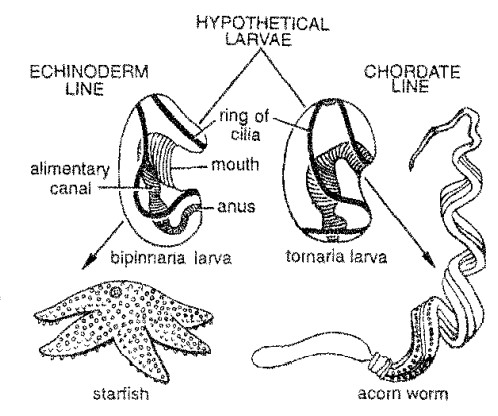
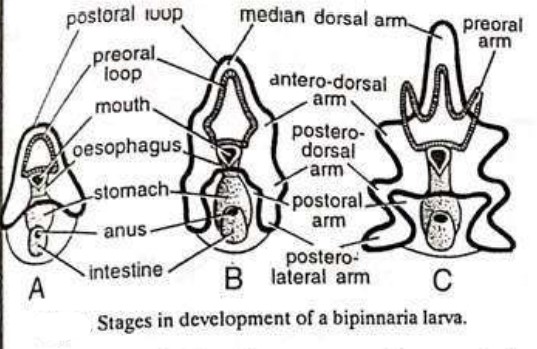
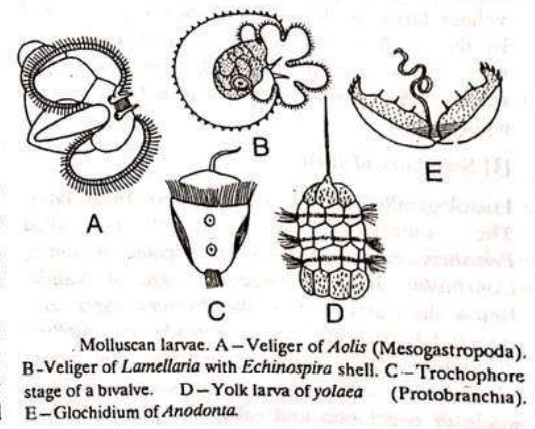
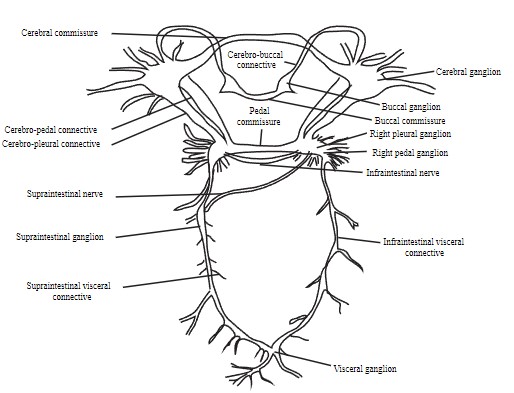
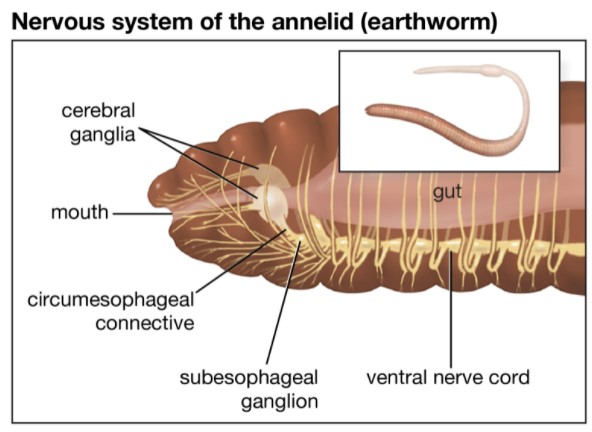
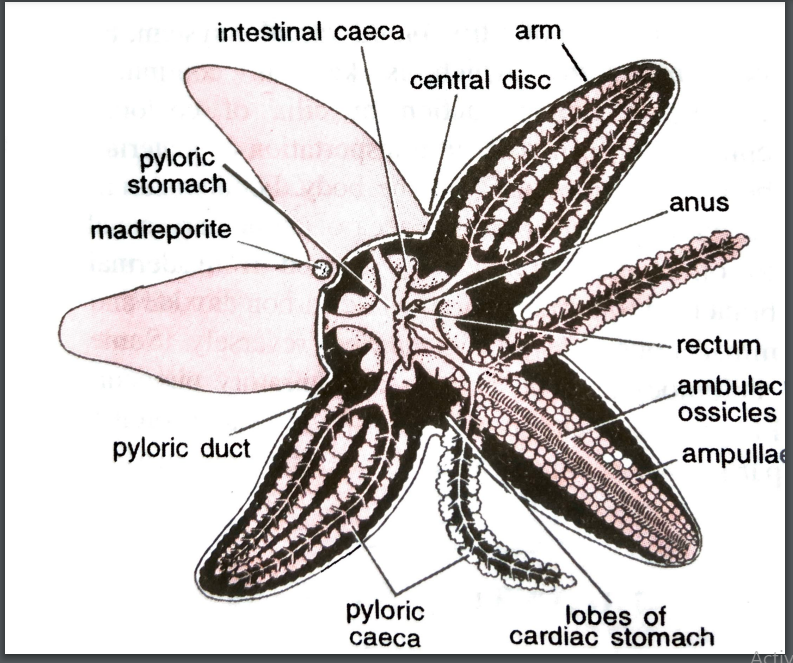
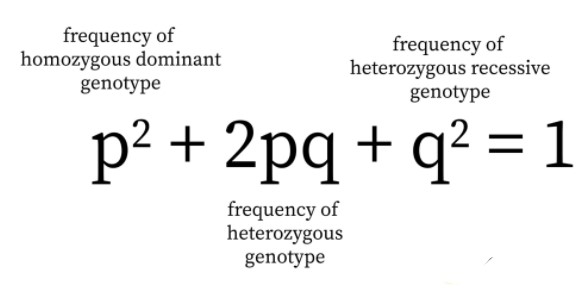WHITE BLOOD CELLS
Introduction White blood cells (WBCs), also known as leukocytes, are the unsung heroes of the human body, tirelessly working behind the scenes to protect us from a myriad of threats. These remarkable cells are the cornerstone of the immune system, acting as the body's primary defense mechanism against infections, diseases,…