DISSECTION OF ASCARIS (ROUND WORM)
General Instructions for Dissection of ascaris (round worm)
While dissecting the animal keep in mind the following points.
- Listen and follow carefully the instructions given by the teacher in your practical class.
- Study well about the internal structures of the animal to be dissected.
- Keep all the instruments in your dissecting box clean and sharp.
- Always keep with you a Zoology Practical Book and also hand-drawn diagram of the dissection.
- Remember that all invertebrates are dissected from dorsal side.
- Wash the animal before dissection to remove excess of formaline or other fixing or killing chemical.
- Keep a white sheet below the animal in dissecting dish.
- Fix the animal in dissecting dish properly. Insert the pins obliquely.
- While opening the animal never make deep incisions as in earthworm, etc.
- Remove the body wall layers in such a manner that all the internal organs are fully exposed.
- Keep your dissection submerged in water.
External features of ascaris (round worm)
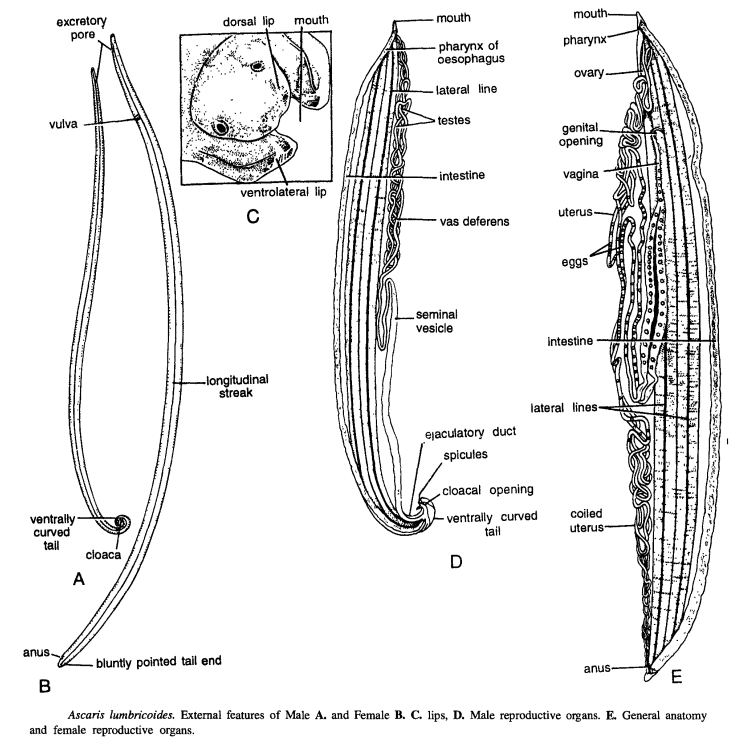
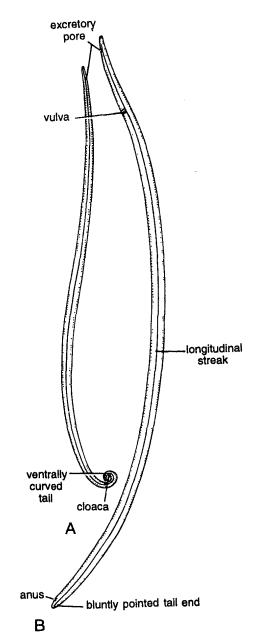
Ascaris is commonly called as round worm. Ascaris lumbricoides is found in the intestine of man, A. suum in the intestine of pig, A. vitulorum in cow and A. megalocephala in the intestine of horse. For studying external features take preserved male and female specimens of Ascaris lumbricoides.
- Mouth and lips: Mouth is terminal, situated at the anterior end. Mouth opening is sillTounded by one dorsal and two ventro-Iateral papillated lips.
- Four longitudinal streaks: Externally the building of hypodermis can be observed as 4 longitudinal dipressions called as streaks on mid-dorsal, one mid-ventral and 2 lateral. The four streaks internally divide the muscles into 4 quadrants.
- Male worm: Male measures 15 to 30 cm in length. The tail end is ventrally curved and contains the mid-ventral cloaca. Sometimes a pair of small copulatory spicules are seen protruding through cloaca.
- Female worm: Female measures 20 to 35 cm in length. Its tail end is bluntly pointed and contains anus. The opening of vulva lies at a distance one third from the anterior end.
- Excretory pore: Anteriorly situated mid-ventrally.
General anatomy Procedure
Take preserved male and female worms. As they are radio-bilaterally symmetrical hence can be dissected longitudinally. Make a fine longitudinal incision in any radius from anterior to posterior end. By forceps fix the flaps of skin in the dissecting dish. Digestive system and reproductive system are dominant structures. Study the following :
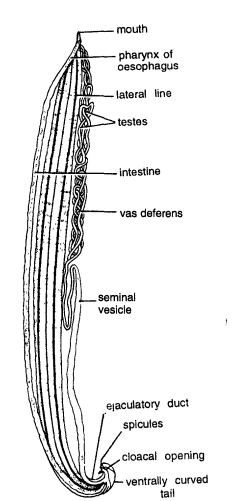
- Digestive system: Both in male and female the digestive system consists of mouth, oesophagus or pharynx and intestine. The intestine occupies major part of the body. The intestine leads into rectum which opens to outside by anus in female and into cloaca in male.
- Excretory canals : In both male and female worms the excretory canals are seen as thin thread like structures on both sides of digestive system.
- Male reproductive system: It contains the following :
- Testis : Monorchic : A single thread-like testis found anteriorly coiled around the pharynx.
- Vas deferens : Testis leads into a wider tube called sperm duct or vas deferens.
- Ejaculatory duct: Vas deferens opens into a short muscular ejaculatory duct posteriorly.
- Cloaca: Ejaculatory duct leads into cloacal chamber which opens to outside by cloacal opening.
- Spicules : The cloacal chamber contains 2 equal spicules or pineal setae. They sometimes project out through cloacal opening. Spicules help in copulation.
- Female reproductive system : It consists of following parts
- Ovaries: Two ovaries coiled around pharynx.
- Oviducts : Each ovary leads into an opaque oviduct.
- Uterus: The oviduct leads into wide uterus. The uterii are very much coiled and occupy major part of the interior. Uterus contains eggs.
- Vagina: The two uterii open into a common chamber called vagina, which opens to outside by vulva.
Discover more from ZOOLOGYTALKS
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

