DISSECTION OF LOLIGO (SQUID)
External features
For dissection of loligo (Squid)Take a nicely preserved specimen. Loligo (Squid) can be easily differentiated from Sepia by having lateral fin in the posterior region of the trunk. Study various structures in head and trunk regions.
Nervous system Procedure
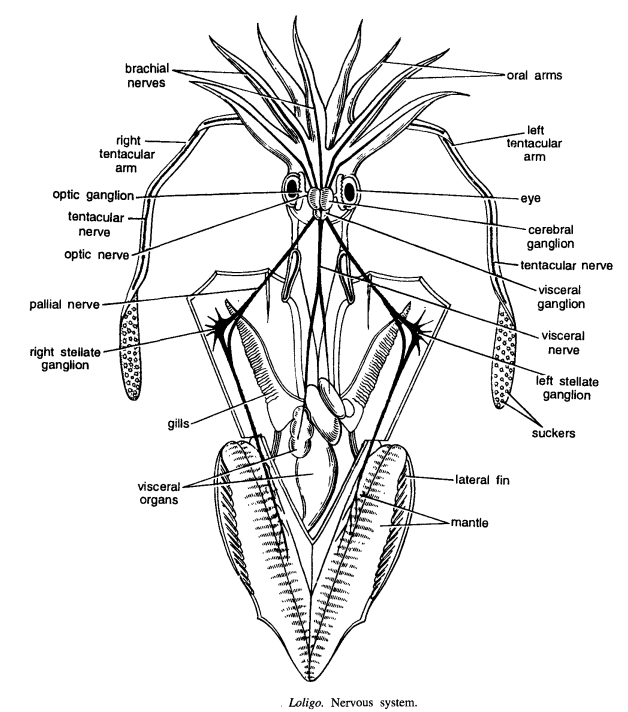
Dissect the animal by making a mid dorsal sagittal incision. Pin the lateral flaps. Expose the cerebral ganglia, visceral ganglion, optic ganglia and stellate ganglia. Carefully trace out the following nerves. Keep black or blue paper below the exposed nerve.
Anterior nerves
- Cerebro-buccal connective: Small nerves from cerebral ganglia originate and connect with superior buccal ganglion just above the brain. These connectives are present under cerebral ganglia.
- Brachial nerves : Eight brachial nerves originate from the pedal ganglionic mass and innervate the mantle.
- Tentacular nerves: Two tentacular nerves originating from the pedal ganglionic mass innervate the tentacles.
- Optic nerves : A pair of optic nerves originating from the lateral side of cerebral ganglia from large optic ganglia on each side. From each optic ganglia small retinal nerves innervate retinal cells.
Posterior nerves
- A pair of pallial nerves : They originate from the posterior side of the visceral ganglion and after running posteriorly form stellate ganglia on each side. Fine nerves from stellate ganglia innervate mantle.
- Visceral nerve : Originate from the posterior portion of the visceral ganglia. After running posteriorly for some distance, divides into two branches. Small branches from each innervate various visceral organs.
Discover more from ZOOLOGYTALKS
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

