DISSECTION OF POECILOCERUS (GRASSHOPPER)
General anatomy of Poecilocerus (Grasshopper) Procedure
For Dissection of poecilocerus (Grasshopper) take either preserved or freshly chloroformed grasshopper. Fix it in the dissecting dish. Cut the lateral membranes between terga and sterna. Remove carefully the cut tergal plates over thorax and head region to study the following systems.
Digestive system of Poecilocerus (Grasshopper) Procedure
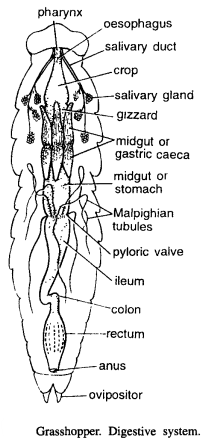
Consists of following parts
- Mouth : Lies in pre-oral cavity and is bounded by labrum, clypeus, mandibles and maxillao. Hypopharynx lies in pre-oral cavity.
- Pharynx : Mouth leads into a short pharynx.
- Oesophagus: Pharynx is followed by a short oesophagus.
- Crop: Oesophagus enlarges into a crop which extends upto thorax. Behind crop is branched salivary gland. Its duct opens into mouth.
- Gizzard: Behind the crop is a small muscular gizzard.
- Midgut: Midgut starts after gizzard and it includes ventriculus or stomach. Anterior end of stomach contains cone-shaped pouches or gastric caeces.
- Hindgut or intestine : Stomach leads into an intestine. At the function of stomach and intestine there are yellowish thread-like Malpighian tubules. Intestine leads into colon. Colon leads to rectum which opens to outsides by anus.
Reproductive system of Poecilocerus (Grasshopper) Procedure
Dissect the grasshopper in same manner as for general anatomy. Carefully examine the male and female reproductive systems. Females are distinguished from the males by the presence of ovipositor at the posterior end of abdomen. Dissect separately male and female insects.
Male Reproductive system of Poecilocerus (Grasshopper)
It consist of following parts
- Testes: Two testes lie in fourth, fifth and sixth abdominal segments. Each testis consists of a series of slender tubules or follicles.
- Vasa deferentia: Each testis leads into vasa efferentia. The vasa efferentia unite to form two sperm ducts or vasa deferentia.
- Ejaculatory duct : The sperm ducts open into a wide duct, called as ejaculatory duct.
- Penis: The ejaculatory duct opens to the exterior through penis.
- Accessory glands and seminal vesicle: On both sides of ejaculatory duct are a number of accessory glands. Associated with accessory glands is a much longer and wider tube called as seminal vesicle for storage of spermatozoa.

Female reproductive system of Poecilocerus (Grasshopper)
Consists of the following parts
- Ovaries : Two ovaries are located over the intestine and connected to dorsal body wall by an ovarian ligament. Each ovary contains 8 ovarioles. Each ovariole contains developing ova arranged in a linear row.
- Oviduct: Each ovary leads into an oviduct.
- Vagina: The two oviducts open into a wide muscular vagina. Vagina opens to outside through the genital opening between the plates of the ovipositor.
- Seminal receptacle or spermatheca : From vaginal pore arises a small tube which communicates with a storage chamber called seminal receptacle.
- Accessory or collateral glands: Lying in front of each oviduct is elongated and curved accessory glands. They secrete a cement like substance that holds the eggs together when laid.
Nervous system Procedure of Poecilocerus (Grasshopper)

Take a freshly chloroformed or preserved grasshopper, cut the wings and fix the animal with dorsal side upwards. Make incision in pleura and remove the tergal sclerites. Remove terga in head region. Now carefully remove the viscera and expose as clearly as possible the entire nervous system. Start from posterior side and gradually trace the nerve cord up to brain. Observe the following parts: Entire nervous system is divided into 3 parts :
- The central nervous system : It consists of a dorsal brain or supra-oesophageal ganglia situated above oesophagus between eyes and connected to ventral sub-oesophageal ganglion by circum-oesophageal connectives sub-oesophageal ganglion is formed by the fusion of mandibular, maxillary and labial ganglia. It gives rise to double ventral nerve cord which extends upto posterior region and shows the following thickenings or ganglia:
- First thoracic ganglion.
- Second thoracic ganglion.
- Third thoracic ganglion
- Five pairs of abdominal ganglia.
- Peripheral nervous system : The following nerves arise from central nervous system :
- A pair of optic nerves originates from optic lobes and supplies to large compound eyes.
- Ocellary nerves: They innervate ocelli.
- A pair of antennary nerves originates from brain and supplies to antennules.
- Walking leg nerves. They originate from thoracic ganglia.
- Abdominal nerves arise from abdominal ganglia and supply to various organs.
- Sympathetic nervous system : It includes occipital ganglion, frontal ganglion and ingluvial ganglion, which are associated with brain and control involuntary actions of alimentation, heart ganglion, frontal aorta and genital organs.
Discover more from ZOOLOGYTALKS
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

