PRIMITIVE NERVOUS SYSTEM OF COELENTERATES AND ECHINODERMS
INTRODUCTION
- The environment and the need of organism is not constant, it fluctuate every time. So every organism need an inbuilt system that allow it to gather information about changing environment and its body need and then allow to respond according. This inbuilt system that detects changes and respond accordingly is a nervous system of an organism.
- The nervous system detects the changes in the environment and then respond to such events. Almost every multicelluar organism possesses nervous system with varying complexity. Only sponges, placozoa and mesozoans lack nervous system.
- Nervous system is basically made up of neurons or nerve cell that are able to sense, receive and transmit information either from one part of the body to other or from external environment to body organs via sense organs.

PRIMITIVE NERVOUS SYSTEM OF COELENTERATES
Hydra
Very primitive type of nervous system is present in Hydra. It include nerve cells or neuron that are bipolar or multipolar lying immediately above the muscle processes and forming an irregular and discontinuous nerve net or nerve plexus. Neighbouring nerve cells are not fused together, but their process or neuritis forms synaptic junctions. Such a nerve net is synaptic nerve net. Nerve cells are numerous around the mouth and pedal disc but show no grouping in the form of nerve controlling centres like brain or nerve ring. A difference from higher animal is that nerve net of hydra is unpolarized so that impulse can pass into all directions.
It has been marked that nerve cells of epidermis and gastrodermis forms two separate nerve net that are interconnected. Their processes are connected to sensory cells, which act receptor for external stimuli, and to epithelio and endothelio muscles cells which act as effector by contracting their muscle processes. Such a combination of muscles cells, sensory cells and nerve net is refer to as neuromuscular system.

Aurelia : A jelly fish
- Nervous system consist of main nerve net, diffuse nerve net and eight rhopalial ganglia.
MAIN NERVE NET
- Nerve cells or fibers are present in each nerve net or plexus. The main nerve net is more develop. It lies on the subumbrellar surface and extend into tentacles, rhopalial, manubrium and oral arms. Its nerve element forms a short ring along the margin of umbrella near the circular canal along per and interradii, main nerve net is somewhat thickened due to the concentration of its nerve element along these radii. Each radial thickening near the margin of umbrella, is connected with rhopalial ganglia situated near the rhopalium on that radius.
DIFFUSE NERVE NET
- Diffuse nerve net lies in the epidermis of subumbrella as well as exumbrella. Its nerve element consist of smaller cell bodies. It also connected with rhopalial ganglia. It controls local responses, like feeding and can inhibit contraction of the umbrella.
RHOPALIAL GANGLIA
- These are formed by aggregation of nerve cells. There are 8 such ganglia one near each sense organ or rhopalium.
- Nerve impulse receive by the sense organs are conducted through nerve net to the muscle fibres which react accordingly.
PRIMITIVE NERVOUS SYSTEM OF ECHINODERMS
Asterias :- A sea star
- It is of simple and primitive type. It formed of nerve net, nerve fibers, and ganglion. At certain places nerve tissue are concentrated to form distinct nerve chord. Their nervous system can be distinguished at four places.
SUPERFICIAL OR ECTONEURAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
It is situated just below the epidermis and consist of following
- Circumoral nerve ring – it is pentagonal and lies in periphery of peristome. It supplies fiber to the peristome and oesophagus. From each angle of the pentagonal circumoral nerve ring arises a radial nerve chord, which runs in the ambulacral groove of its corresponding arms and terminates into sensory cushion at base of terminal tentacles.
- Five radial nerves – supplies fibers to tube feet and ampullae.
- Subepidermal plexus – it is in the form of elaborated nerve net in each form :-
-
- It connects to the radial nerve chord by fine nerve fibers.
- It forms a pair of adradial or marginal nerve one along each margin of the ambulacral groove.
- It forms nerve ring in sucker of each tube foot.
- It contains sensory as well as motor fibers. Thus is serve for to receive and coordinate response, like a central nervous system of other animals.
DEEP OR HYPONEURAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
It consist of following parts :-
- Double circumoral ring situated on the oral side just above the main or ectoneural nerve ring
- Five pairs of langes nerve which arises from the former and extent into the arms, one pair in each. Each extend as plate of nerve tissue in the outer oral wall of radial hyponeural sinus and sends out branches to the muscle of arm.
- The deep nervous system arises from mesoderm and its primary function is of motor.
ABORAL OR COELOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
- It is represented by thin nerve plexus situated in a aboral body wall, just above the parietal layer of coelomic epithelium. It somewhat thickened to form an anal nerve ring in central disc and nerve in each arm. Aboral nervous system is connected with the marginal nerve by several lateral nerve in each arm.
- It is also mesodermal in origin as well as motor in nature.
VISCERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
- It possesses well defined nerve plexus situated in the gut wall. It innervate the muscles of gut wall and is connected visceral receptor.
SENSE ORGANS
1. Neurosensory Cells
- They are distributed throughout the epidermis, specially concentrated at the sucker of the podia. Neurosensory cells are of two type one is tactile and other is olfactory. Tactile is more abundant in tube feet and olfactory around the mouth.
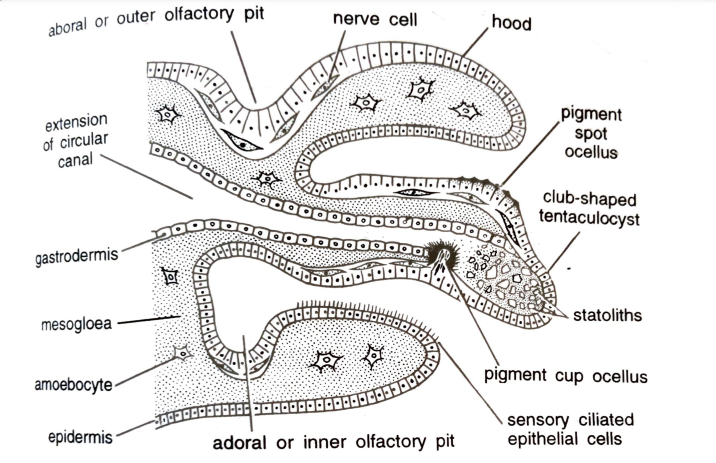
2. Eyes
- Sea star possesses five bright eye spots, one at the end of each arm at base of terminal tentacles, on the oral side. Eye spot detect changes in the light intensity.
![FIGURE DEPICTING Sea star [A] Section through terminal tentacles and eye spot [B] V.S of single eye pit](https://www.zoologytalks.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/0-4.png)
CONCLUSION
Nervous system in Coelenterata and Echinoderm is not complex. Hydra and jelly fish possesses diffused nervous system, diffused nervous system is most primitive form of nervous system. Nerve cells are distributed beneath the outer epidermis. Brain is absent though there can be concentrated neuron present locally and ganglia are present. This kind of nervous system is just beginning in the evolution of nervous system.
Echinoderms also possesses very simple nervous, consist of a simple nerve ring and five radial nerves that supplies fibers to tube feet and ampullae. Here also brain is absent neither any structure similar to brain is present. Most part of nervous system is of mesodermal origin. Neurosensory organs and eye spot act as sensory organ.
Discover more from ZOOLOGYTALKS
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

