Slide Preparation of Porifera (Sponge and Gemmules)
Introduction
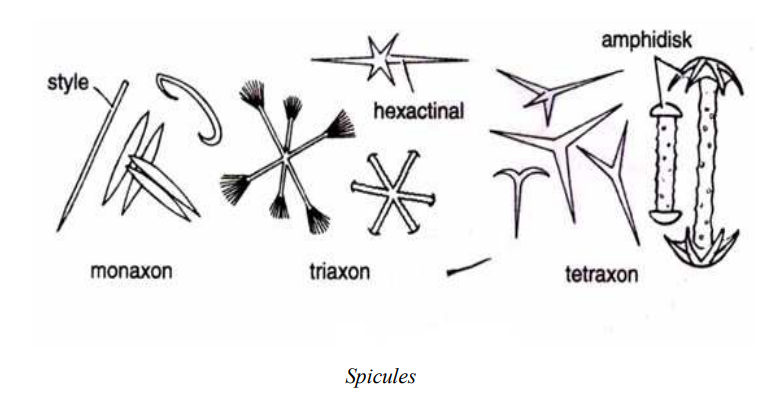
The body wall of sponges is supported by various minute crystalline and calcareous bodies called as spicules. These are secreted by special mesenchymal cells called scleroblasts.
Spicules provide taxonomic characters and are classified according to the axas and rays called as axon, actine and actinal respectively. These are of two types:
- Megascleres-Support skelton
- Microscleres-Smaller and none supporting.
- These are of following types
- Monaxon-consist of single axix,straight or curved
- Tetraxon-Consist of four rays
- Triaxon-consists of three axes
- Polyaxon-Having several equal rays
- Spicules generally support and protect the body and helps in identification classification and metabolism.
Method for Slide preparation
For extraction of spicules, boil a small portion of sponge in 15-20%potassium hydroxide solution in a test tube till cells are dissolved. The spicules settle in the bottom. Decant the KOH solution and wash the spicules several times in tap water. Pass the spicules in ascending series of alcohol, 30%, 50%, 70%, 90% and 100% alcohol. Dealcoholize or clear with xylol and mount on a slide after pipetting the spicules. There is no need of staining. Study under the microscope and note different type of spicules as monaxon, triaxon, tetraxon etc.
Comments
- Sponge body wall is supported by various minute, crystalline and calcareous bodies called as spicules, which are secreted by special mesenchymal cells called as scleroblasts.
- Spicules provide taxonomic character and are classified according to the axes and rays, spoken of as axon, actine or actinal respectively.
- Spicules are of two types: (i) Megascleres or supporting skeleton, (ii) Microscleres small and non supporting. Kinds of Megascleres are as follows;
- Manaxon consists of a single axis, straight or curved. They may be styles, rhabds and tylots.
- Tetraxon consists of four rays. It also includes triradiate or triactinal spicules.
- Polyaxon having several equal rays. Amphidisk spicules are found in fresh water sponges. In this type, the rhabdom contains disks at both ends. The arrangement of different types of spicules could be seen in Sycon.
- Microscleres are found throughout the mesenchyme and include spires and asters.
- Spicules support and protect the body. They are helpful in identification, classification and metabolism.
Identification
The clear transparent monaxon or triaxon spicules indicate Spicule of sponges.
Gemmules
Gemmules are asexual reproductive bodies forming a part of regular life cycle. These are endogenous buds which are diagnostics of Porifers, especially of freshwater and a few marine sponges. Gemmulation or endogenous budding is a peculiar mode of reproduction under unfavourable condition such as excessive cold or drought.
Comments
- Gemmules are asexual reproductive bodies forming a part of regular life-cycle .
- Gemmules or endogenous buds are diagnostic of Porifera and especially of fresh-water and a few marine sponges.
- Gemmulation or endogenous budding is a peculiar mode of reproduction under unfavourable conditions such as excessive cold or draught.
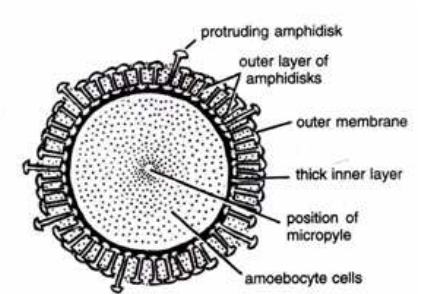
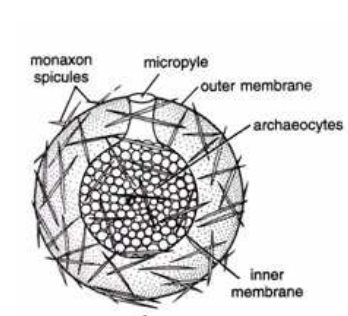
- Gemmules contain outer and inner membrane.
- Gemmule is rounded structure formed by the aggregation of archaeocytes into groups accompanied by trophocytes which are impregnated with food particles of glycoproteins or lipoproteins.
- Scleroblasts secretes the amphidisk spicules, which forms a row in columnar layer between outer and inner membrane
- Gemmules are resistant to external factors such as freezing and drying. Gemmules of fresh water sponge can be kept for 2 years.
- They hatch at a temperature of 13-21◦C in about 3 days. After hatching, a gemmule gives rise to a young sponge.
- A full grown gemmule is usually pierced by opening on one side, called a micropyle.
Identification
Since the material has micropyle in mature and amphidisk spicules in immature gemmules and has above all features, hence it is Gemmule whole mount.
Discover more from ZOOLOGYTALKS
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

