Classification of Balantidium
Phylum :-Protozoa – (Unicellular)
Sub-phylum :- Ciliophora – (Cilia movement in all stages.)
Class :- Ciliata – (Cilia present throughout life.)
Sub-Class :- Euciliata – (Cytopharynx, contractile vacuole, mega-and micronucleus present)
Order :- Spirotricha -(Adoral membranelles extending around peristome in clockwise direction.)
Genus :- Balantidium
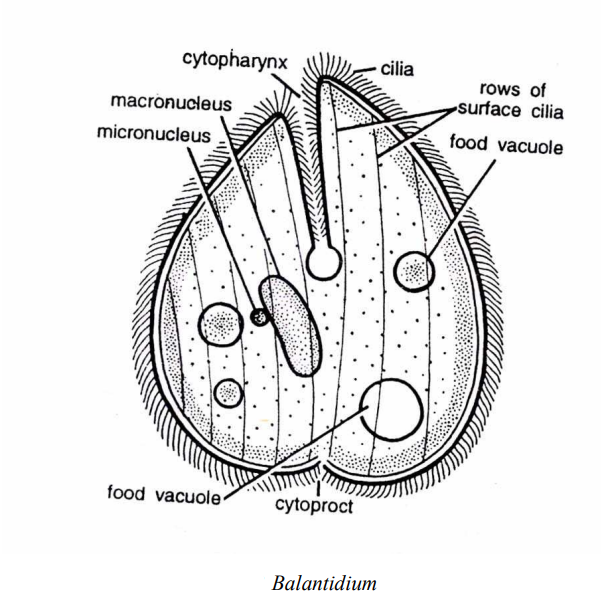
General Study of Balantidium
Balantidium is commonly found in the intestines of pigs, sheep, camels, opossums, ostriches, cockroaches and man. It is abundantly found in the rectal content of the from Balantidium is a ciliate parasitic in the large of pigs, monkeys and man. Some species are parasitic in frog, fish, cockroach and horse. It is an egg-shaped animal pointed at the anterior end and rounded posteriorly.
The body has longitudinal rows of small cilia. At the anterior end is a peristome with longer cilia, below the peristome is a mouth leading into short cytopharynx with no cilia ( B. entozoan).
There is a large sausage-shaped macronucleus obliquely in the middle of the body, and in its concavity near it is a small micronucleus. Unlike most parasitic protozoa there are two contractile vacuoles, one near the middle and a larger one at the posterior end.
There are several food vacuoles containing human erythrocytes and fragments, it also ingests starch and yeast from the colon of the host. At the posterior end is a permanent cytoproct.

Reproduction is by transverse binary fission and occasionally by conjugation in which there is an exchange of nuclear material and reorganization of the macronucleus, this is followed by binary fission.
The parasite also forms thick-walled cysts, but no multiplication takes place in the cyst. In human beings Balantidium coli causes ulcers and haemorrhage in the colon and caecum, which cause chronic dysentery.
These parasites can be removed by administering small doses of aureomycin and terramycin for 10 to 15 days.
Balantidium is now placed in subclass Holotrichia, order Tricho stomatida and not with Spirotrichia because
- Its peristomial ciliature develops from body kinetia which during binary fission form an incomplete band stronger and longer cilia below the middle of the body, while in Spirotrichia the peristomal ciliature develops wither from previous oral kinetosomes or from stomatogenetic kinetia.
- It has no oral membranelle or buccal ciliature which are conspicuous in Spirotrichia.
Economic status
The pathogenic species is Bcoli, found in the colon of men, monkeys and pigs. It causes ulcers and dysentery. The natural host for B. coli is the pig in which it is transmitted in the encysted state. Human beings who handle pigs become infected by the cysts. The cysts react with intestinal epithelium where they cause pathological changes. B. coli of pigs serve as biological control for nematode larvae.
Identification
Since the parasite has slit like vestibule and all above feature hence it is Balantidium.
Discover more from ZOOLOGYTALKS
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

